In c# 4.0, the new dynamic type has been introduced to bypass the type checking at compile-time. Instead, it will resolve the type at runtime. In c#, the dynamic type is same as implicitly typed local variable var, but the only difference is the type checking will happen at runtime.
We can define dynamic type variables using a dynamic keyword like as shown below.
In the above declarations, we used a dynamic keyword to define the dynamic variables. In most cases, the compiler will compile the variables of dynamic type into the object type variables, but the compiler does not resolve those during compile-time; instead, those will evaluate at run time.
The above dynamic declarations will be compiled into object types during compile-time, as shown below.
As discussed, the actual type will assign to the dynamic variables at runtime based on the right-side value of the initialization statement.
The following example will show how to declare dynamic variables and how a dynamic variable will change its type based on the right-side value of its initialization statement.
If you observe the above example, we declared and initialized the dynamic variables with different values. The actual type will assign to the dynamic variables at runtime based on the right-side value of the initialization statement.
When we execute the above example, we will get the result as shown below.
If we use dynamic type as a method parameter, then it will accept any type of parameter at run time.
Following is the example of using dynamic type as a method parameter in c#.
If you observe the above example, we defined the GetDetails method with a dynamic parameter so it will accept any type of parameter; that’s why we call the GetDetails() method by sending different types of values.
When we execute the above example, we will get the result as shown below.
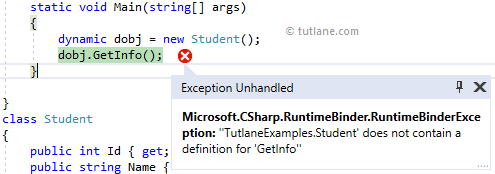
In c#, if we assign any class object to a dynamic type, the class object properties and methods will be exposed only at runtime. So, the compiler will not throw an exception even if we try to access the methods or properties which do not exist in the class.
Following is the example of assigning the class object to dynamic type and accessing properties and methods in c#.
If you observe the above example, we created a dynamic variable “dobj” and assigned the User class object. We tried to access the GetInfo() method that does not exist in the User class. However, the compiler will not throw an exception because it will skip the type checking for dynamic type during compile time, but we will get a runtime exception as shown below.
The following are the important points that we need to remember about dynamic type in c#.
dynamic type is useful to bypass the type checking at compile-time. Instead, it will resolve the type at runtime.dynamic type as a method parameter, then it will accept any type of parameter at run time.