In visual basic, yield is a keyword and it is useful to indicate that the method, operator or property in which it appears is an iterator.
Following is the syntax of defining the Yield keyword in visual basic.
Yield expression
In the above statements, the Yield statement will return one element at a time and the return type of Yield keyword must be always IEnumerable or IEnumerator object of values.
The Yield statement is not allowed to use in anonymous methods and in the methods that contain unsafe blocks.
The declaration of Yield must meet the following requirements.
Yield statement can be used in the try block of try-finally statement.Yield statement can be used in Try or Catch block but not in Finally block.In visual basic, we can consume the iterator method that contains a Yield statement either by using For Each loop or LINQ query.
In For Each loop, each iteration will call the iterator method, and the iterator method will return an expression when a Yield statement is reached, and the current location of code is retained to restart the code execution from that location the next time the iteration method is called.
Following is the example of defining the Yield statement in a method that’s inside of For Each loop to return the required values.
Module Module1
Sub Main(ByVal args As String())
For Each i As Integer In Multiply(2, 10)
Console.Write("{0} ", i)
Next
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
Public Iterator Function Multiply(ByVal number As Integer, ByVal range As Integer) As IEnumerable(Of Integer)
Dim result As Integer = 1
For i As Integer = 1 To range - 1
result = result * number
Yield result
Next
End Function
End Module
If you observe the above example, we created Multiply() method with a Yield statement that’s inside of For loop and each iteration of the For Each loop will call the iterator method (Multiply) until it reaches Yield statement and the return type of iterator method we used is IEnumerable of int.
Here, the iterator method (Multiply) will return the value after executing the Yield statement and the current location of code is stored to restart the code execution from that location the next time when the iteration method is called.
So for the first time, the Multiply method will execute all the lines of code, next time the execution of the iterator body continues from the location (within For loop) where it left off like as shown below.
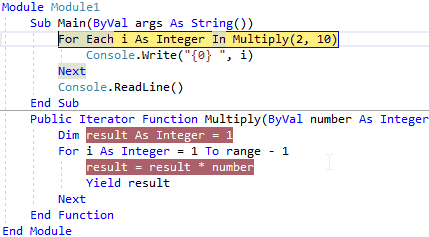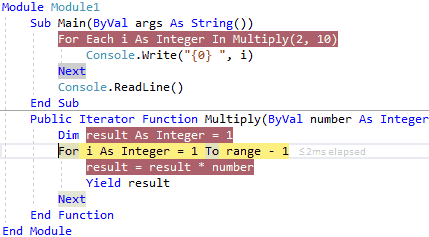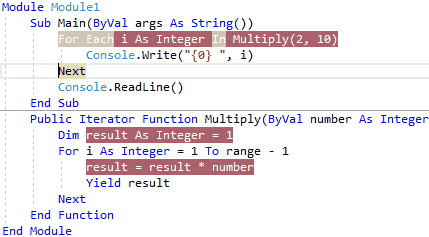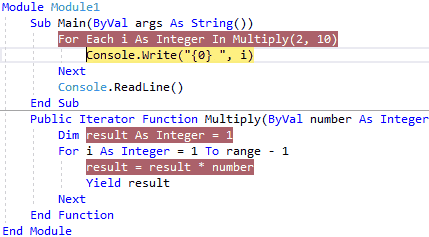
When we execute the above example, we will get the result like as shown below.
This is how the Yield keyword is useful to reduce the lines of code execution in visual basic.
Following are the important points which we need to remember about yield keyword in visual basic.
Yield is a keyword and it is useful to indicate that the method, operator or property in which it appears is an iterator.Yield <expression>.Yield statement is allowed to use in anonymous methods and in the methods that contain unsafe blocks.Yield statement can be used in the Try block of try-finally statement.Yield statement either by using For Each loop or LINQ query.