In SQL, the SOME operator compares a value with a single column set of values returned by the subquery. The SOME operator in SQL must match at least one value in a subquery, and that value must be preceded by comparison operators.
Generally, we will use this SOME operator in the WHERE clause to check whether the required column values match with the set of values returned by the subquery or not.
Following is the syntax of using some operator in the SQL server.
If you observe the above SQL SOME operator syntax, we will get values only when column1 values match with column1 data returned by subquery otherwise, it will not return any data.
We will check some operator with examples for that create “EmployeeDetails” table by using the following script in your SQL database.
When we execute the above script, a new table called “EmployeeDetails” will be created, and the result will be as shown below.

Now execute the following examples to check how SOME operator will work in SQL Server.
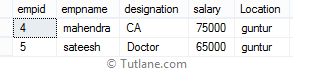
The following SQL statement will return employee details whose salary column values match with the data returned by the subquery.
When we execute the above SQL query, we will get the result as shown below.
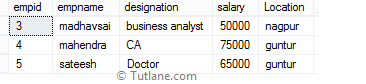
The following SQL statement will return employee details whose salary column value matches with at least one value with the data returned by subquery, and that value must be preceded by comparison operators.
When we execute the above query, we will get the result below.